As 2025 crests into focus, central processing units (CPUs) remain one of the fundamental engines of our digital world. But, as a developer with 5 years of experience, I have seen CPUs evolve rapidly over the past several years to become more powerful, flexible, and still the fundamental computing “brains.” Today, we’ll take a look at how these fundamental pieces work, recent developments, and applications across various industries.
Understanding the Digital Brain
At its most basic level, the CPU works using the fetch-decode-execute cycle — the universal process that allows computers to execute programs and calculate. This cycle occurs billions of times per second in today’s processors across seven essential stages:
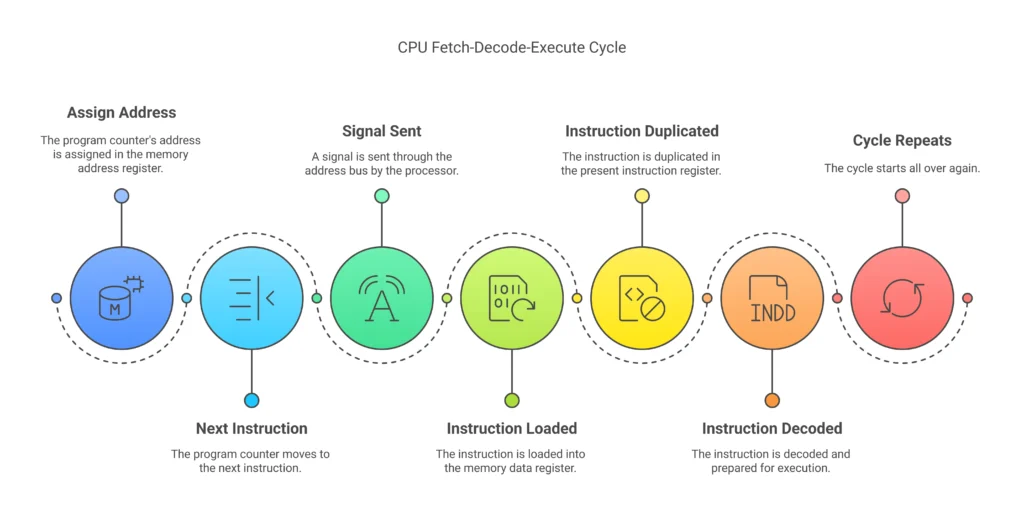
- The address of the program counter is assigned in the memory address register
- The program counter now goes to the next instruction
- A signal is sent through the address bus by the processor
- It will be sent to the memory data register
- This instruction is duplicated in the present instruction register
- For each instruction, it is decoded and executed
- Paraphrase the sentence( I am your new cycle ) The cycle starts all over again)
This simple process is the backbone of everything from basic calculations to advanced AI workloads. This core function is now extremely improved due to the introduction of multi-core architectures and rising clock speeds.
Multi-Core Architecture and Parallel Processing
Modern high-performance CPUs take advantage of multiple processing cores to run tasks in parallel. This is Intel’s 2025 mobile high end, with the Core Ultra 9 275HX comprising 24 cores (8 P and 16 E cores) with a maximum frequency of 5.4GHz. This hybrid architecture—mixing and matching different kinds of cores—picks up on the industry trend toward specialized processing units built into the CPU itself.
Beyond Moore’s Law: The Evolution of CPU Technology
For decades, Moore’s Law governed the predictable growth of computing power. But as we near atomic limits of silicon transistors, the industry has taken a more nuanced perspective.
This pragmatic perspective was voiced in mid-2024 by Dr. Kevin Zhang of TSMC: “I don’t care whether Moore’s Law is alive or dead. I don’t care, so long as we continue to push the edge of technology scaling.” This marks a clear departure away from the pure transistor-density arms race of the past, and one more in line with overall system performance.
The Shift to 3D Integration
With conventional 2D scaling hitting physical limits, the industry turned to 3D integration approaches. It’s worth noting that TSMC has been keen to stress that PPA improvements from generation to generation with the transition to a given process node are now well over 30%. If in the past this progress was achieved by miniaturizing transistors, it’s now derived from increasingly complex three-dimensional chip packaging and heterogeneous integration.
AI Integration in Modern CPUs
AI acceleration capabilities have been increasingly integrated directly in designs by CPU manufacturers. Intel Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX) provide a dramatic performance boost for deep learning workloads on Intel Xeon Scalable processors with no need for separate accelerator hardware. This functionality allows CPUs to seamlessly process AI tasks such as natural language processing, recommendation engines, and image recognition.
Trending Innovations: Reshaping CPU Architecture
Chiplets & Modular Design
Dominance of monolithic CPU design has been replaced by modular “chiplet” architectures. Intel’s Meteor Lake processors are a prime example of this strategy with its six different pieces; package substrate, CPU tile, GPU tile, IO Extender tile, and SOC tile.
Benefits of chiplet design include:
- Higher yields by producing smaller components
- Supports mix of process nodes for different components
- Increased product line cross-scaling
- Improved power distribution for dedicated elements
Neuromorphic Computing: Brain-Inspired Processors
Neuromorphic computation is a radical new paradigm in processor design based on biological neural networks. We are going to solve this with neuromorphic, which unlike the classical von Neumann, they have incredible energy efficiency and real-time adaptability.
Intel’s Loihi 2 is a prime example of this, and its Hala Point system has a larger scaffolding on which to play—1,152 Loihi 2 processors that collectively support 1.15 billion neurons and 128 billion synapses, which make it the largest neuromorphic system to date.
RISC-V: The Open-Source CPU Revolution
We are already seeing the rapid establishment of RISC-V ISAs based on open-source hardware, which have built significant momentum compared to the proprietary x86 and ARM architectures. The China Xiangshan project, run by the Chinese Academy of Sciences, presents an advanced RISC-V processor in 2025.
The project’s leader laid out their ambition around a project that they dubbed “ the Linux of processors,” hinting at a future where open-source CPU designs become mainstream.
Modern Applications: CPUs at Work

Edge Computing: Processing at the Point of Need
Edge computing — performing data processing near its point of generation rather than in a cloud-based data center — has changed the way we look at data-intensive applications. According to Gartner, 75% of enterprise data will be processed out on the edge by 2025, up from just 10% in 2018.
Such a dramatic shift demands CPUs that emphasize efficiency and work on restricted workloads. The convergence of 5G networks and improved AI in edge devices allows for applications such as:
- Autonomous vehicles
- Smart healthcare
- Industrial automation
- IoT device networks
VR and AR: Powering Immersive Experiences
High-end CPU’s are often required for VR and AR applications that need to generate sophisticated environments in real time and with low latency. VR and AR ARE STANDARD FOR VIRTUAL COLLABORATION (2025) Companies start using VR and AR for virtual collaboration.
Retail applications use AR in “try-before-you-buy” experiences and virtual showrooms, and education and training programs implement VR for immersive learning.
Web3 and Decentralized Computing
Web3 technologies — what serves the idea of decentralization, blockchain, and user ownership — uses distributed CPU resources across a network, instead of centralized servers. Web3 allows direct communication and transfer through the internet without the need for third-party mediation; however, in early 2025, decentralized applications still need computational power, including CPUs, to perform cryptographic operations, consensus mechanisms, and so on.
Energy Efficiency & Sustainability: Computing’s Green Future

Low-Power CPU Designs
The ultra-low-end processor in ARM’s portfolio is its Cortex-M0+ core, which is aimed at power-sensitive sensors, wearables and other types of power-constrained use cases. This fast 32-bit processor gets performance on par with old desktop CPUs while still operating in the power envelope of 8-bit microcontrollers.
Code density is an ARM processor strong point, limiting memory footprint, making the most of on-chip Flash memory leading to lower cost and power.
ARM processors’ exceptional code density significantly reduces memory requirements, maximizing on-chip Flash memory usage and reducing both cost and power consumption.
Innovative Cooling Solutions
Thermal management also becomes all the more critical, as CPUs get increasingly powerful. Graphene-based cooling solutions are promising for how to get rid of heat in ever-tinier chip designs.
“You can use graphene, an extremely thin, pancakes-like, 2-D material that can be miniaturized, to cool down hot spots forming heating problems in your chip,” says Eva Y. Andrei, a Rutgers University physics professor. “This solution has no moving parts and is very efficient for cooling.”
Security Challenges: Protecting the Brain
Hardware Vulnerabilities
The 2018 discovery of Meltdown and Spectre vulnerabilities revealed fundamental security flaws in processors designs as old as 1995:
- Meltdown (CVE-2017-5754) allows malicious users to read only privileged memory
- Spectre (CVE-2017-5753 and CVE-2017-5715) stealing info from kernel or cache
These vulnerabilities stem from speculative execution, a performance optimization technique in modern processors. Although patches have now been developed, they do reduce system performance by between 5-30%, exposing the complicated balance that needs to be made with regards to security.”
Future Directions: Beyond Silicon
Biological Computing and BCIs
Possibly the most revolutionary move away from traditional CPU architecture is biological computing. Announced in March 2025, the CL1 biological computer combines living human brain cells and silicon hardware within a hybrid biological computing system classified as “Synthetic Biological Intelligence” (SBI).
This novel approach allows human neurons generated from induced pluripotent stem cells to grow on a silicon chip with a 59-electrode array to communicate with biological and digital systems. This being presented is a essential wherefore will be represents for potential Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs) that changes how we interact with a digital world.
I’m a developer working in this field and have witnessed firsthand how BCIs are moving from medical technology to consumer tech. Biological computing combined with conventional CPUs could someday:
- Allow direct neural control of devices
- Make human-computer interaction more intuitive
- Create prosthetics with unparalleled accuracy
- Explore novel avenues for treating neurological diseases
HPC for Scientific Discovery
High-performance computing (HPC) systems increasingly combine traditional CPU-based processing with specialized accelerators for all sorts of complex scientific problems. The deployment of two CPU-based supercomputers in India—Arka (11.77 petaFLOPS) and Arunika (8.24 petaFLOPS)—highlights how these systems facilitate essential applications such as climate modeling and disaster preparedness.
This delivery moves from many global supercomputers which use GPUs to enhance performance; these systems on go another approach, relying on CPUs exclusively, with over 5,000 compute nodes driven by AMD EPYC processors powering them.
Genomics and Personalized Medicine
Genomics and personalized medicine are also flavours of the future aided by advanced CPU technologies. Thanks to the intersection of AI and genomics, the following can be achieved:
- Personalized therapies determined by specific genetic profiles
- Australian Institute of Population Genomics
- Effective handling of large biological datasets
Driving this growth, collaborations between academic institutions, biotech companies, and healthcare providers are projected to surpass an $80 billion market by 2025.
Comparing CPU Architecture Approaches
| Architecture Type | Key Benefits | Best Applications | Energy Efficiency |
| Traditional Multi-Core | Versatility, software compatibility | General computing, desktop applications | Moderate |
| Hybrid (P-core/E-core) | Balance of performance and efficiency | Mobile devices, laptops | High |
| Neuromorphic | Real-time adaptability, extremely low power | Robotics, AI, edge computing | Very High |
| Chiplet Design | Optimized components, flexible manufacturing | High-performance computing, servers | Moderate to High |
| Biological Integration | Novel computing paradigms, BCI development | Experimental applications, neural interfaces | Varies |
The Evolving Brain of Digital Systems
As we approach the second half of 2025, CPUs have evolved far beyond their original function of being basic calculation engines. They are now the brains at the center of increasingly sophisticated, mixed, computing systems driving everything from tiny embedded devices to gargantuan supercomputers and next-generation artificial intelligence at platforms.
This sudden progress opens exciting new opportunities for developers like myself that work at the intersection of hardware and software. Whether you’re writing next-generation applications, pushing the boundaries of AI, or just trying to figure out what makes your devices tick, knowledge of CPU technology is more worthwhile than ever.
What CPU advancements are you most looking forward to? Comment Below 🤔 What are your thoughts?
Pingback: Brains of Computer: Power of CPUs in Modern Technology - Exploring the Future of Brain-Computer Interfaces & AI
Pingback: The Mind-Machine Revolution: How Brain-Computer Interfaces Are Changing Our World - Exploring the Future of Brain-Computer Interfaces & AI
I found your blog site on google and test just a few of your early posts. Continue to maintain up the excellent operate. I just additional up your RSS feed to my MSN Information Reader. Searching for forward to reading extra from you later on!…